4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol
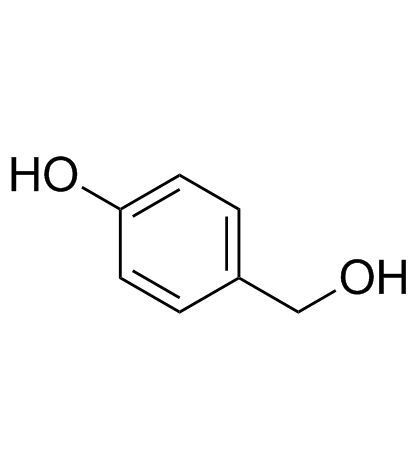
4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol structure
|
Common Name | 4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 623-05-2 | Molecular Weight | 124.137 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 252.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H8O2 | Melting Point | 114-122 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 145.8±15.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol is a phenolic compound widely distributed in various kinds of plants. Anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-nociceptive activity. Neuroprotective effect. Inhibitor of tumor angiogenesis and growth[1][2][3][4]. |
| Name | p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol is a phenolic compound widely distributed in various kinds of plants. Anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-nociceptive activity. Neuroprotective effect. Inhibitor of tumor angiogenesis and growth[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | 4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol inhibits proliferation of eEND2 cells and suppresses the migration of eEND2 cells, accompanied by inhibition of actin filament reorganization[2]. 4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol induces apoptotic death of tumor cells[3]. |
| In Vivo | 4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol possesses antiangiogenic, anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activity possibly via its down-regulating activity on NO production[1]. 4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol (200 mg/kg) efficiently inhibits growth and angiogenesis of developing tumors[3]. 4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol ameliorates ischemic injury induced by transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats, and this neuroprotective effect may be partly related to attenuate apoptosis pathway[4]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 252.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 114-122 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H8O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 124.137 |
| Flash Point | 145.8±15.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 124.052429 |
| PSA | 40.46000 |
| LogP | 0.30 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.596 |
| InChIKey | BVJSUAQZOZWCKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | OCc1ccc(O)cc1 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DA4796800 |
| HS Code | 29072900 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2907299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2907299090 polyphenols; phenol-alcohols。supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward)。VAT:17.0%。tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:5.5%。general tariff:30.0% |
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of structurally diverse compounds with β-cyclodextrins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009) This paper reports a QSAR study for predicting the complexation of a large and heterogeneous variety of substances (233 organic compounds) with beta-cyclodextrins (beta-CDs). Several different theoret... |
|
|
High tolerance and physiological mechanism of Zymomonas mobilis to phenolic inhibitors in ethanol fermentation of corncob residue.
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 112 , 1770-82, (2015) Corncob residue as the lignocellulosic biomass accumulated phenolic compounds generated from xylitol production industry. For utilization of this biomass, Zymomonas mobilis ZM4 was tested as the ethan... |
|
|
Predicting the substrate specificity of a glycosyltransferase implicated in the production of phenolic volatiles in tomato fruit.
FEBS J. 278(2) , 390-400, (2011) The volatile compounds that constitute the fruit aroma of ripe tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) are often sequestered in glycosylated form. A homology-based screen was used to identify the gene SlUGT5, w... |
| 4-(Hydroxymethyl)benzolol |
| (4-Hydroxyphenyl)methanol |
| Gastrodigenin |
| p-Methylolphenol |
| 4-hydroxymethyl-phenol |
| PARA-ALCOHOLPHENOL |
| 4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol |
| 4-hydroxybenzyl-alcohol |
| Benzyl alcohol, p-hydroxy- (8CI) |
| p-(Hydroxymethyl)phenol |
| p-Hydroxybenzyl |
| 4-(Hydroxymethyl)phenol |
| RARECHEM AL BD 0098 |
| EINECS 210-768-0 |
| Benzenemethanol, 4-hydroxy- |
| Benzyl alcohol, p-hydroxy- |
| 4-METHYLOLPHENOL |
| benzyl alcohol, 4-hydroxy- |
| P-HYDROXYBENZYL ALCOHOL |
| MFCD00004658 |
| 4-HYDROXY-BENZYL-ALCOHOL |
| α-Hydroxy-p-cresol |
| FEMA 3987 |
| Bisoprolol Impurity 19 |
 CAS#:123-08-0
CAS#:123-08-0 CAS#:105-13-5
CAS#:105-13-5 CAS#:4397-53-9
CAS#:4397-53-9 CAS#:99-76-3
CAS#:99-76-3 CAS#:110-89-4
CAS#:110-89-4 CAS#:120-47-8
CAS#:120-47-8 CAS#:3256-45-9
CAS#:3256-45-9![[4-(Hydroxymethyl)phenyl]boronic acid Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/251/59016-93-2.png) CAS#:59016-93-2
CAS#:59016-93-2 CAS#:166544-95-2
CAS#:166544-95-2![[4-(2-Chloroethoxy)phenyl]methanol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/408/111728-87-1.png) CAS#:111728-87-1
CAS#:111728-87-1 CAS#:103-87-7
CAS#:103-87-7 CAS#:35421-08-0
CAS#:35421-08-0 CAS#:55779-48-1
CAS#:55779-48-1 CAS#:3897-89-0
CAS#:3897-89-0 CAS#:4403-71-8
CAS#:4403-71-8 CAS#:696-60-6
CAS#:696-60-6 CAS#:3597-91-9
CAS#:3597-91-9![[4-(diethoxyphosphorylmethoxy)phenyl]methanol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/296/143056-54-6.png) CAS#:143056-54-6
CAS#:143056-54-6
